Industry information
Company News
- Aluminum veneer customization, creating a new trend of personalized space
- Honeycomb aluminum plate: a perfect combination of lightweight and sturdy
- Aluminum veneer customization, creating a new trend of personalized space
- Aluminum veneer: the beauty of industry, simple yet not simple
- Aluminum veneer customization, creating a new trend of personalized space
Industry dynamics
- Aluminum honeycomb panel: a perfect combination of lightweight and sturdy
- Honeycomb aluminum plate: a lightweight choice, revealing the new favorite of industrial materials
- Aluminum ceiling, creating a new trend of fashionable home furnishings
- Is aluminum veneer suitable for high-rise buildings?
- Analysis of Color Stability of Aluminum Veneer
Frequently asked questions
- How can aluminum veneer improve the appearance of buildings?
- Has the production process of aluminum veneer reduced energy consumption?
- Can the insulation function of aluminum veneer solve the structural problems of buildings?
- Can aluminum veneer be used in the design of building arch bridges?
- What is the manufacturing process of aluminum veneer?
contact us
Mobile:+86 15627778610
Email: 2201229786
Address: No. 5 Binjiang Road, High tech Zone, Zhaoqing City, Guangdong Province
Selection of surface treatment for aluminum veneer
- Author: Lesilong Technology (Guangdong) Co., Ltd
- Release time: 2022-03-18 18:55:33
- Click:0
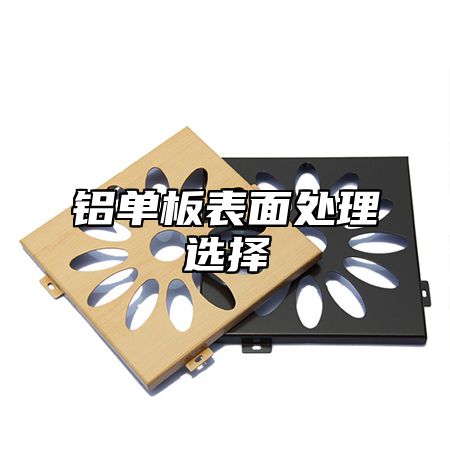

Aluminum veneerIt is a commonly used building material, and its surface treatment has a significant impact on its service life and aesthetics. Different surface treatment methods will bring different effects, so when choosing aluminum veneer, it is necessary to choose according to actual needs. This article will provide a detailed introduction to several common surface treatment methods and their characteristics for aluminum veneer.
1、 Anodizing
Anodizing is a commonly used surface treatment method for aluminum veneer, which forms an oxide film on the surface of the aluminum veneer through electrolytic oxidation. This processing method can improve the corrosion resistance and wear resistance of aluminum veneer, while also increasing its surface hardness and glossiness, making it more beautiful.
2、 Fluorocarbon spraying
Fluorocarbon spraying is a high-end surface treatment method for aluminum veneer, which forms a uniform, smooth, and colorful coating on the surface of the aluminum veneer by spraying fluorocarbon coating. This processing method has excellent weather resistance and UV resistance, and can be used outdoors for a long time without fading.
3、 Heat transfer printing
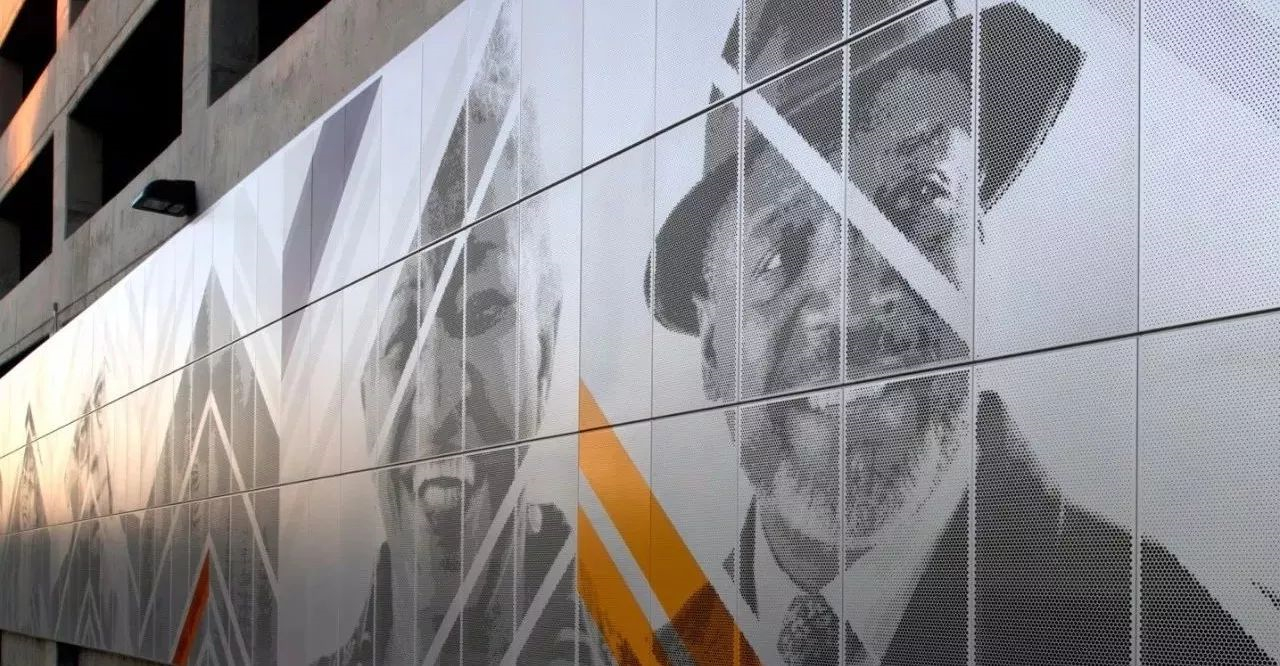
Heat transfer printing is a method of transferring patterns or text onto the surface of aluminum veneer, which can be achieved through high temperature and high pressure to create a permanent decorative effect. This processing method is suitable for occasions that require personalized customization, such as billboards, signs, etc.
4、 Wire drawing oxidation
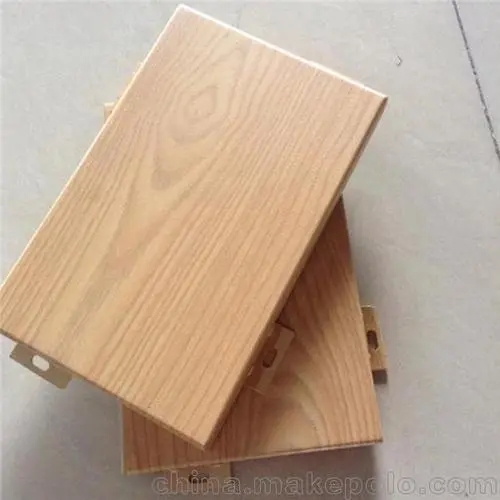
Wire drawing oxidation is a method of grinding the surface of aluminum veneer into fine filaments through mechanical processing, and then subjecting it to oxidation treatment. This processing method can create a unique texture effect on the surface of aluminum veneer, enhancing its visual impact and decorative effect.
5、 Hollow carving
Hollow carving is a method of cutting the surface of aluminum veneer into various shapes and patterns through mechanical processing, and then subjecting it to oxidation treatment. This processing method can achieve various complex decorative effects, such as relief, carving, etc., and is suitable for the high-end architectural decoration field.
6、 Conclusion
There are many surface treatment methods for aluminum veneer, each with its own characteristics and applicable scope. When selecting aluminum veneer, it is necessary to choose according to actual needs to ensure that it achieves the expected effect. At the same time, attention should be paid to the influence of different surface treatment methods on the performance of aluminum veneer, such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, weather resistance, etc.






 Customer service QQ
Customer service QQ